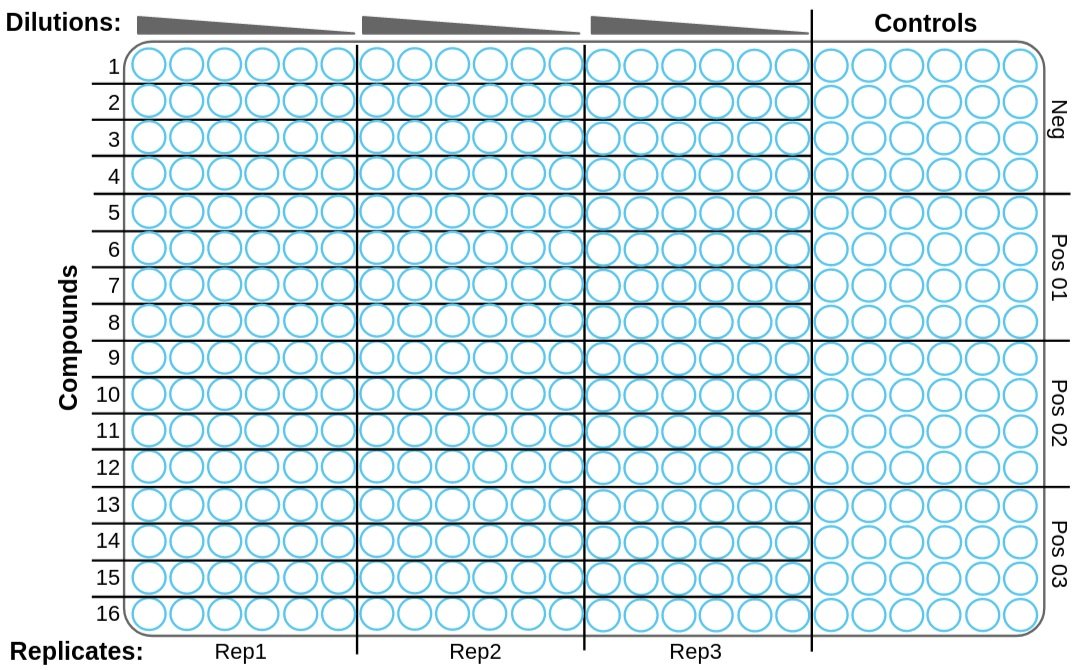
AutoHCS is simple and easy to use. It can work flexibly on different cell lines, compound types, and experimental layouts. Training AIs to score high-content screens requires the following guidelines:
AutoHCS guidelines
For data collection:
2-3 replicates
4 or more concentrations per compound
1 negative control and 1 or more positive controls
16 or more images per condition
For imaging:
20x objective
5x5 image grid per well on 96-well plates / 3x3 on 384-well plates
1 or more channels (brightfield, +/- 1+ fluorescent channels)
Example layout: 384-well plate, 16 compounds with 6 concentrations (3 replicates), 4 controls (3 positive, 1 negative)
Training the AI: Controls
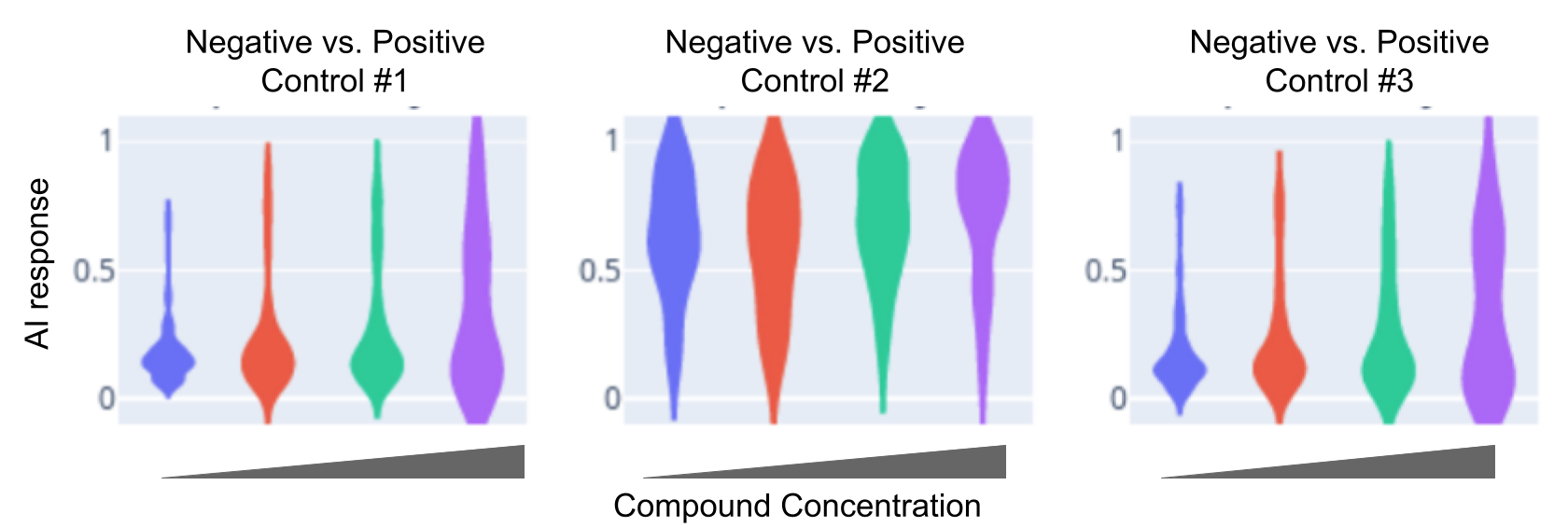
Following image upload to the servers, AutoHCS trains a binary AI on each of the positive controls against the negative control. This produces a confusion matrix demonstrating true and false positives and negatives.
These control AIs can be used to score compounds in reference to each of the positive controls.
Another AI is trained on all controls to produce a dendrogram and similarity matrix demonstrating varying phenotypes within the positive controls.
This All-Control-AI can be used to compare compound concentrations by phenotype similarity.
Training the AI: Compounds
An AI is trained for each compound across all concentrations and the negative control. Scoring these independently of the positive control permits the discovery of novel phenotypic responses.
Here you can see that there is a dose-dependent response to this compound. If this response is significantly different than that of the positive controls, this result would be lost in a simple comparison against positive and negative controls.
The Report
Following image upload, AutoHCS delivers a report consisting of two sections. First, the AI Validation Section demonstrates the validation of the trained AIs using control samples. This will demonstrate high performance on true-positives and true-negatives. It will also show similarity of positive controls using matrices and dendrograms.
Second, the Compound Scores Section highlights the AIs score dose-response for each compound. In the below example, three compounds are demonstrated. The top compound is most similar to positive control #3. The middle compound does not have a visible effect (a negative result). The bottom compound has a dose-dependent effect, but demonstrates a phenotypic effect unaccounted for by the available positive controls.
Lastly, in the All-compound comparison section, all the high doses of each compound are compared to each other to generate a dendrogram of phenotypic similarity. The main clusters are color-coded. This clustering can provide mechanistic insights as compounds targeting similar cellular pathways would be expected to yield similar phenotypes.
Participate in a pilot screen
Join ViQi’s team of scientists to find out how your drug screening process can improve in both speed and sensitivity with AutoHCS. Contact us to become a hands-on collaborator for our pilot screening program and receive a report scoring your high-content screen.
If you are unsure if AutoHCS can meet your needs but interested in our product, please contact us anyway. AutoHCS can scale from mini screens with limited data to large screens with thousands of compounds and all are useful towards the continuing development of this assay. We are excited to work with you.